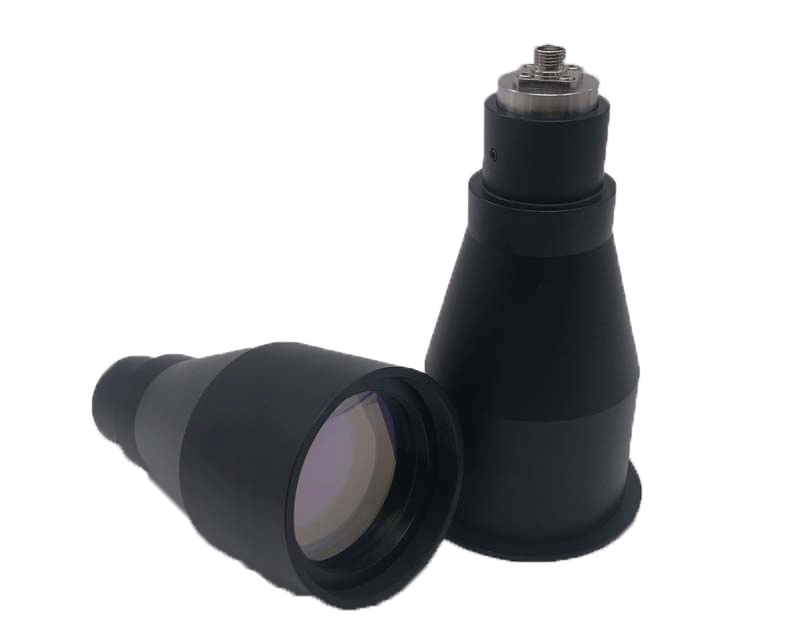
Introduction
In modern optics, collimating lenses play a crucial role in shaping beams of light. Whether in lasers, fiber optics, radiology, or telescopes, collimation ensures that light rays are parallel, improving precision and efficiency.
At Bote, we specialize in designing and manufacturing custom collimating lenses for research, medical imaging, and industrial applications. This article provides a comprehensive guide on collimating lenses, their meaning, types, applications, and costs.

Collimating Meaning: What Is a Collimator?
The term collimation refers to aligning light rays so they travel parallel without converging or diverging.
- Collimating meaning: The process of shaping light into a parallel beam.
- What is a collimator? A collimator is any optical device (lens or mirror) designed to produce collimated light.
In practice, a collimating lens is used to transform divergent light from a point source (like a laser diode or LED) into a well-defined beam.
How Does a Collimating Lens Work?
A collimating lens works by:
- Taking light from a point or small source.
- Positioning the source at the focal length of the lens.
- Outputting light rays that emerge parallel.
Collimating lens focal length: The focal length determines the degree of collimation. Shorter focal lengths create tighter beams, while longer focal lengths produce wider but more stable collimation.Essential for microbiology and fine structure imaging.At Bote Optical, we provide cost-effective, customized beamsplitter solutions. Contact us for a quotation tailored to your specifications.👉 For a full list of materials and coatings, see our Custom Infrared Optics page.
Types of Collimating Lenses
1. Telescope Collimator
Used in astronomy, telescope collimators ensure optical alignment of mirrors and lenses for sharper images.
2. Collimation in Radiology
In medical imaging, collimators control the shape and size of X-ray beams, reducing patient exposure and improving image contrast.
3. Fiber Optic Collimator
Essential for coupling light into and out of optical fibers, reducing divergence and loss.
4. Collimating Lens for LED
LEDs naturally emit divergent light. Collimating lenses improve brightness, directionality, and efficiency in illumination systems.
5. Laser Collimating Lens
Lasers require precise collimation to maintain beam quality over long distances.
- Laser diode collimating lens: Corrects the divergence from semiconductor laser chips.
- Aspheric collimating lens: Minimizes spherical aberrations, ensuring higher precision.
 Coating Machine
Coating Machine
Collimating Lens vs Focusing Lens
While both lenses manipulate light, their purposes differ:
| Feature | Collimating Lens | Focusing Lens |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Makes light rays parallel | Brings rays to a focus point |
| Application | Lasers, LEDs, fiber optics | Microscopy, imaging, projection |
| Output | Collimated beam | Focused spot |
👉 In many systems, collimating and focusing lenses are used together for beam shaping.
How to Make a Collimated Beam
To create a collimated beam:
- Place the light source (laser diode, LED, or fiber output) at the focal point of the lens.
- Adjust the lens position until the output rays run parallel.
- Use an aspheric collimating lens for better accuracy.
At Bote, we provide precision optical design services to help engineers achieve the ideal beam profile for their applications.

Collimating Lens Price
The cost of collimating lenses varies by material, coating, and precision.
| Type of Collimating Lens | Typical Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Plastic LED Collimators | $1 – $20 |
| Glass Laser Collimating Lens | $30 – $200 |
| Aspheric Collimating Lens | $100 – $500 |
| Custom Collimating Lens (Bote) | On Request |
For custom requirements (UV, IR, or laser optics), contact Bote for tailored solutions.
Applications of Collimating Lenses
- Laser systems: Laser cutting, medical lasers, communications.
- LED illumination: Automotive headlights, projectors, flashlights.
- Fiber optics: Telecommunications, sensors.
- Radiology: X-ray beam collimation.
- Astronomy: Telescope mirror alignment.
 Inspecting by Interferometer ZYGO
Inspecting by Interferometer ZYGO
FAQ: Collimating Lenses
Q1: What is the function of a collimating lens?
It transforms divergent light into a parallel beam, ensuring high-quality optical performance.
Q2: What is the difference between collimating and focusing lenses?
Collimating lenses create parallel light, while focusing lenses converge light to a spot.
Q3: Can I use a collimating lens for both LEDs and lasers?
Yes, but the design and coating requirements differ. Bote provides optimized designs for each.
Q4: Why use an aspheric collimating lens?
To minimize aberrations and achieve higher beam quality, especially in laser systems.
Q5: How do I choose the right collimating lens?
Consider focal length, wavelength range, material (glass, plastic, IR crystal), and application.

Conclusion
The collimating lens is a cornerstone in optical systems, from laser diodes to radiology. Understanding its meaning, working principle, and applications helps engineers and researchers design more efficient systems.
At Bote, we provide customized collimating lenses and advanced optical solutions, whether for fiber optics, LED lighting, infrared imaging, or laser applications. Contact us today for tailored designs.
Related Reads:
- What Is Interferometry?
- High-Precision IR Filters | Custom Infrared Bandpass Filters for Optical Systems
- Spherical vs Aspherical: Optical Design Tips
Boost your optics performance with custom aspheric lenses—engineered for precision, designed for excellence.