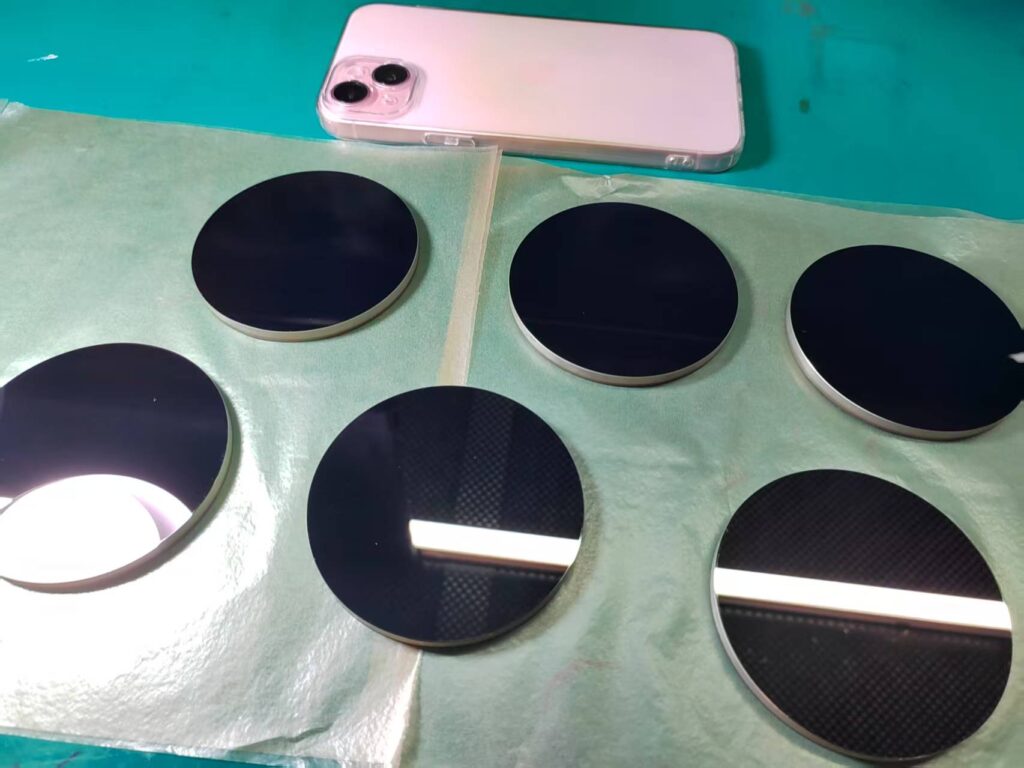
What Is Germanium & What Is Germanium Used For?
Germanium is a rare element with unique optical and electronic properties. It plays an important role in infrared optics, fiber optics, solar energy, and semiconductor applications. This article covers everything you need to know about germanium: its properties, uses, origins, refining process, price trends, and why it matters today — especially in the context of global supply chain shifts.

What Is Germanium?
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, grayish-white metalloid that belongs to the carbon group on the periodic table. Germanium is similar to silicon but has superior performance in certain infrared and electronic applications.
Is Germanium a Metal?
Germanium is not a true metal. It is classified as a metalloid, meaning it has properties of both metals and non-metals. This hybrid nature is what makes it so valuable in high-tech applications.
Germanium Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Symbol | Ge |
| Atomic Number | 32 |
| Melting Point | 938.25°C (1720.85°F) |
| Boiling Point | 2833°C (5131.4°F) |
| Appearance | Shiny, gray-white |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate (semiconductor) |
| Transparency (IR) | High from 2μm to 16μm |
Germanium is transparent to infrared light, making it ideal for infrared windows and lenses used in thermal imaging and surveillance systems.

Where Is Germanium Found?
Germanium is not mined as a standalone ore. It is typically extracted as a byproduct of zinc, copper, and lead mining, especially from sphalerite ores. The top producers of germanium include:
- China (by far the largest)
- Russia
- Canada
- Belgium
Because of its limited sources and complex refining process, germanium is considered a critical material.
Germanium Refining Process
Germanium is refined through multiple steps:
- Extraction – Recovered as a byproduct from mining residues.
- Roasting & Leaching – Zinc smelter residues are treated to extract germanium compounds.
- Purification – Germanium tetrachloride (GeCl₄) is purified by distillation.
- Reduction – GeCl₄ is reduced with hydrogen to produce pure germanium metal.
- Zone Refining – Ultra-pure germanium is further refined for semiconductor applications.
At Bote, we work with refined germanium blanks and polished windows, and provide precision IR lens fabrication with tight tolerances.

Why Is Germanium Important?
Germanium is essential in defense, energy, telecommunications, and infrared optics.
- Infrared Optics: Germanium windows and lenses are used in thermal cameras, night vision, drones, and gas detection systems.
- Semiconductors: Germanium is a key material in high-speed electronics and transistors.
- Solar Cells: Used in high-efficiency satellite and space-grade photovoltaic systems.
- Fiber Optics: Germanium dioxide is used to dope fiber cores to improve signal performance.
Germanium vs Silicon
| Feature | Germanium (Ge) | Silicon (Si) |
|---|---|---|
| Bandgap | 0.66 eV | 1.12 eV |
| Electron Mobility | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| IR Transparency | Excellent | Poor |
| Semiconductor Usage | High-speed, niche | Mainstream |
While silicon dominates consumer electronics, germanium is better for infrared optics and high-frequency electronics.

Germanium Uses in Everyday Life
Although germanium isn’t found in everyday household products, it supports the systems behind many modern technologies:
- Thermal scopes for firefighters and military
- Night vision goggles
- Infrared sensors in medical devices
- Telecom fiber networks
- Space solar panels
At Bote, we supply high-precision germanium windows, lenses, and blanks to support these industries globally.
Germanium Semiconductor Type
Germanium is an intrinsic semiconductor, meaning it conducts electricity better than insulators but not as well as metals. It becomes even more useful when doped with elements like arsenic (n-type) or gallium (p-type). This makes it ideal for:
- Transistors
- Diodes
- Integrated circuits
Though silicon has replaced it in most applications, germanium is still used in niche, high-performance electronics.
Germanium Stone Price & Market Trends
Germanium is not a gemstone, but high-purity germanium for optics and semiconductors is priced based on purity and form.
📈 Germanium Price Chart (Estimated)
| Year | Price per kg (99.999% purity) |
|---|---|
| 2020 | $1,100 |
| 2022 | $1,500 |
| 2023 | $1,950 |
| 2024 | $2,200+ (due to global demand) |
Prices are influenced by China’s export policies, demand from defense and tech industries, and overall supply chain disruptions.
Why Is Germanium Named “Germanium”?
Germanium was discovered in 1886 by German chemist Clemens Winkler. He named it after his homeland, Germany (Germania in Latin), to honor its discovery. Ironically, today China controls most of the supply.
Germanium in Chinese
In Chinese, germanium is written as 锗 (pinyin: zhě). It is classified as a rare metal and is regulated for export from China.
🌍 Why Bote Is Your Reliable Source for Germanium Products
Under the current US-China trade tension, importing germanium raw materials from China has become highly restricted. Exporters must undergo strict approval, and many overseas buyers face long delays or rejections.
✅ Our Advantage:
At Bote (bote.com.sg), based in Singapore:
- We hold proper export licenses and can ship germanium lenses, blanks, and windows to the US, Europe, and other markets without delay.
- Our engineering team supports custom specifications and fast prototyping.
- We inspect each component using state-of-the-art interferometers and spectrophotometers.
Interesting Facts About Germanium
- Used in early transistors before silicon took over.
- Transparent to infrared but opaque to visible light.
- Critical material in US and EU resource security lists.
- Small amounts are also used in alloys and plastics.
Conclusion
Germanium is a rare, strategic material that continues to play a vital role in modern technology — from infrared optics to space tech. At Bote, we help bridge the gap between tight global supply and rising demand, especially in markets like the USA where sourcing from China is restricted.
Looking for a trusted germanium optics supplier?
Contact us today — we deliver precision and compliance from Singapore to the world.